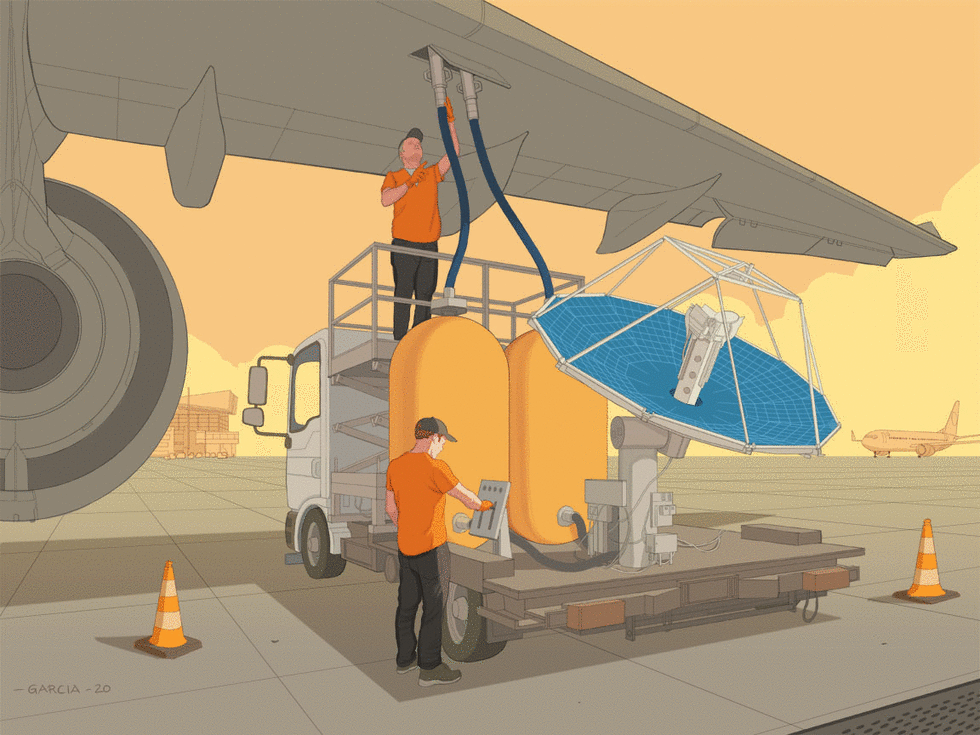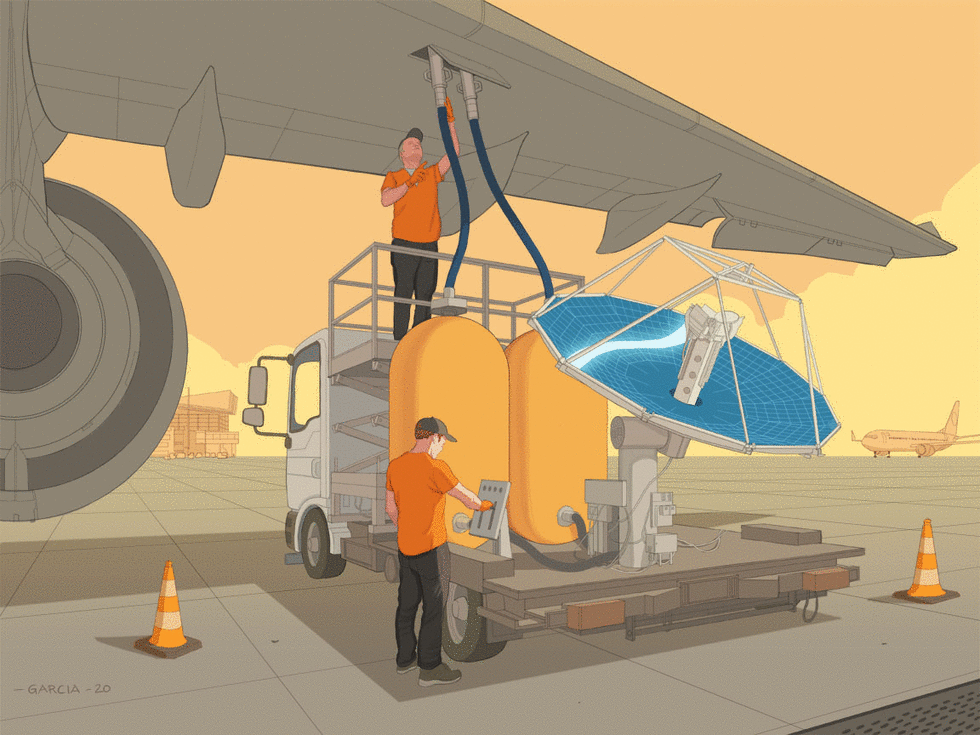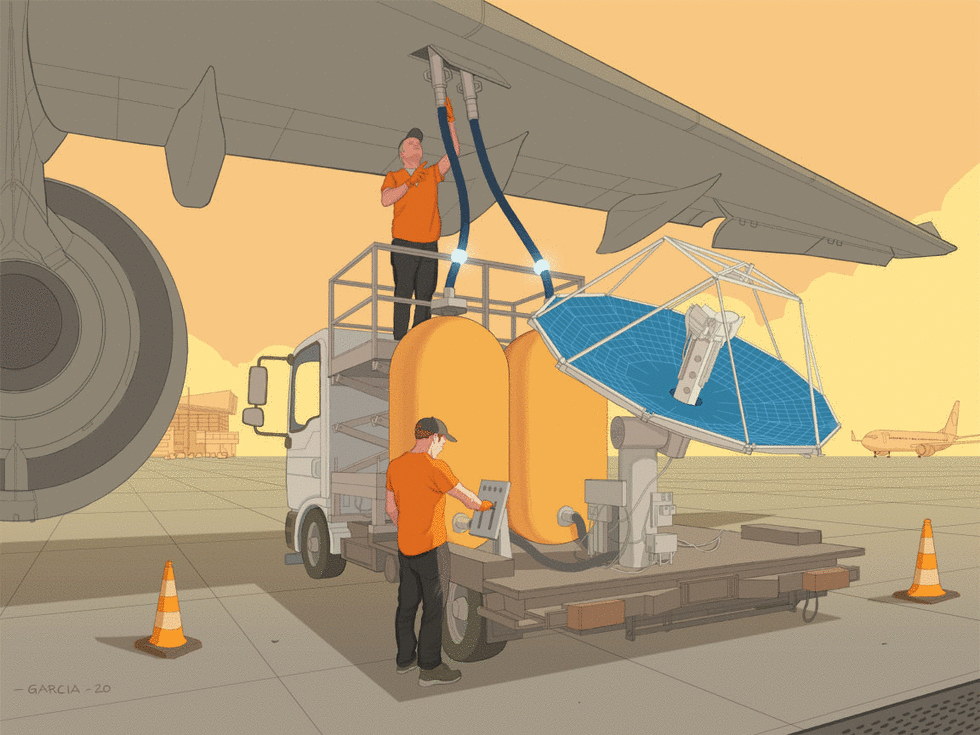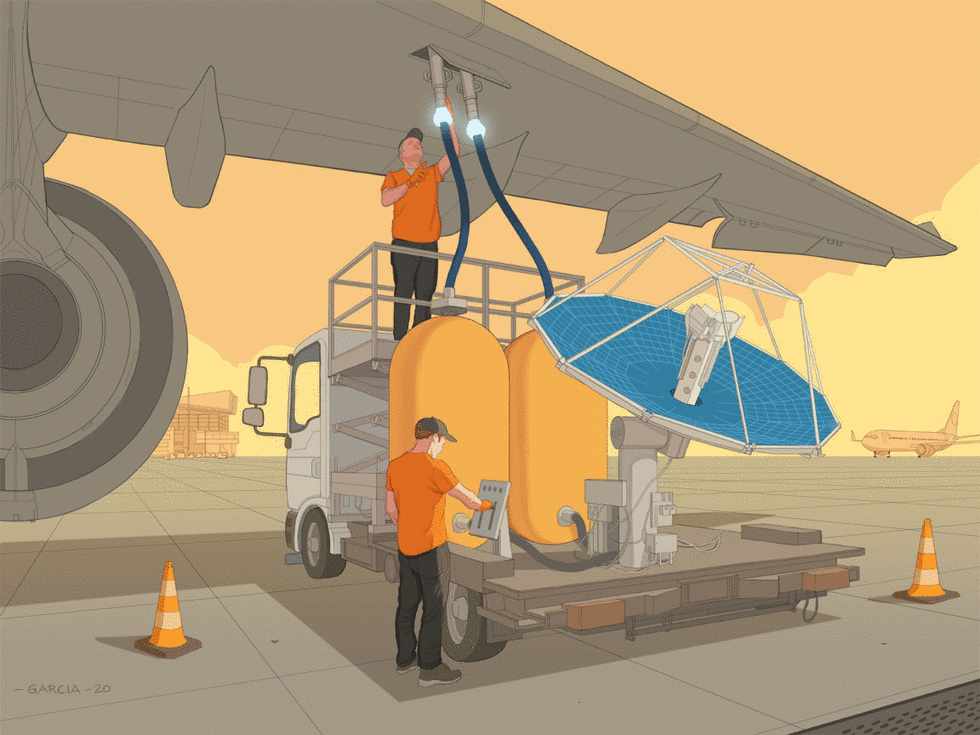
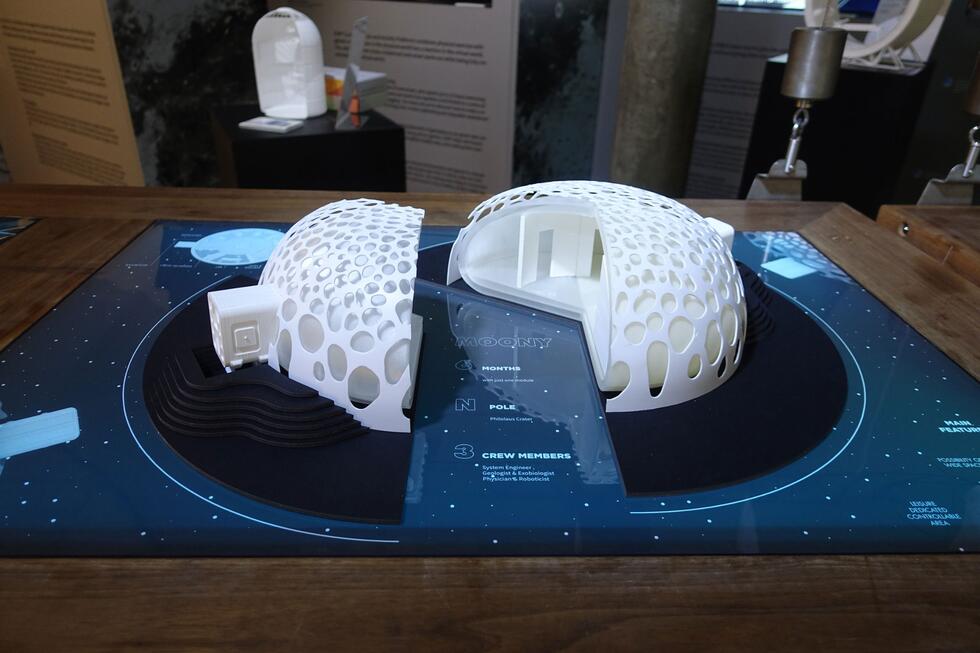
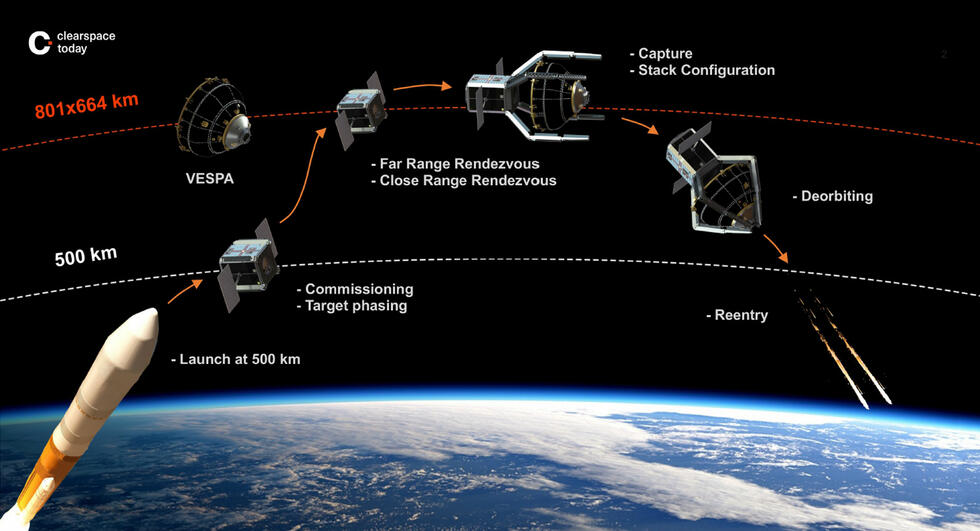
SHORT NEWS
Surgery from a distance
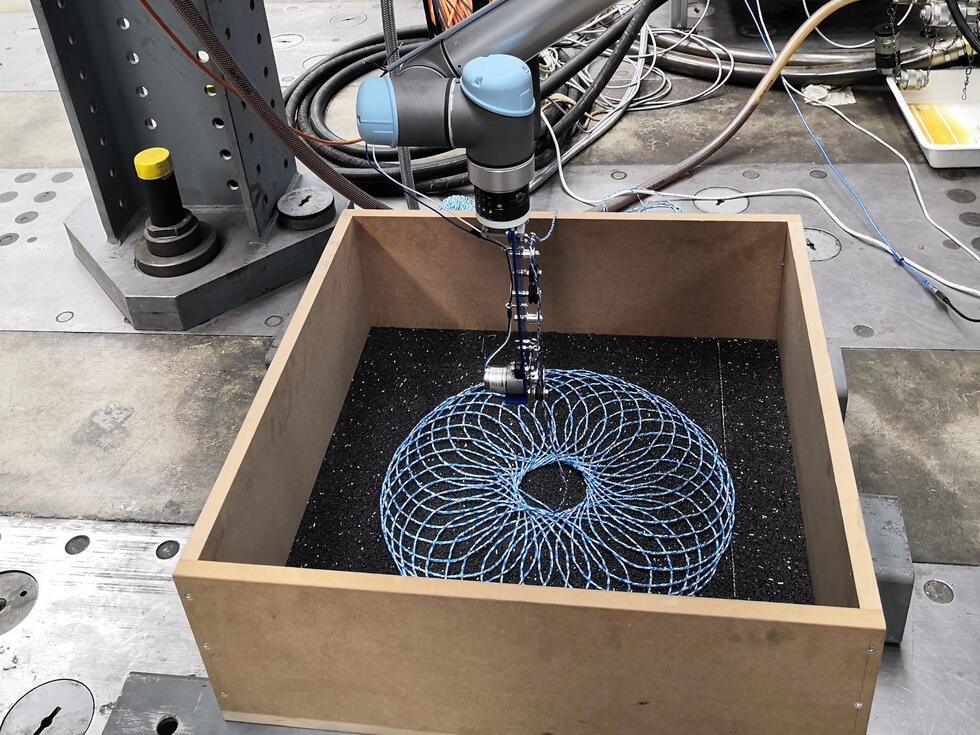
A joystick-controlled robot could help surgeons operate on stroke patients remotely. This would allow patients to be treated during the critical time window after a stroke - even if they are far away from a specialist.
After a stroke, it is important to act quickly. But neurovascular surgeons often work in large medical facilities that are difficult for patients in remote areas to reach. A system developed by MIT researchers could allow patients to receive endovascular treatment remotely during the critical window of time after a stroke. The research team envisions that its robotic system could be installed in smaller hospitals and controlled remotely by trained surgeons in larger medical centres.
Using a modified joystick, surgeons in a large hospital could control a robotic arm in another location to operate on a patient in a timely manner. This could save the patient's life and preserve brain function.
The robotic system, whose movement is controlled by magnets, is designed to remotely assist in endovascular procedures - a procedure performed in emergency situations to treat strokes caused by a blood clot. Such procedures usually require a surgeon to manually guide a thin wire to the clot, where he or she can physically remove the blockage or administer drugs to dissolve the clot.