SHORT NEWS
Ammonia as a drive for more sustainable shipping
Shipping leaves a large ecological footprint: the propulsion engines are largely dependent on energy sources that produce climate-damaging CO2 when burnt. In addition to hydrogen and methanol, ammonia is also considered a more climate-friendly substitute fuel.

Worldwide, pollutant emissions must be lowered and the emission of climate-damaging substances reduced. However, according to current studies, a rapid increase in global energy demand and transport volume is diagnosed. The fight against the climate crisis therefore also starts with transport on the high seas. Shipping is therefore well advised to replace fossil liquid or gaseous fuels with alternative fuels.
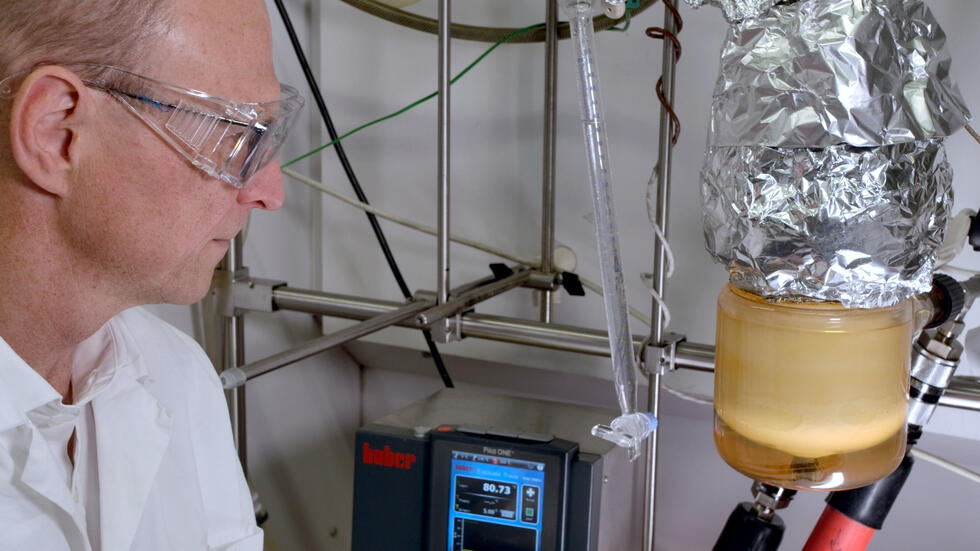
The LEC research institute at Graz University of Technology is actively involved in the global search for alternatives. For more than 20 years, it has been researching ways to reduce harmful emissions from large engines. The LEC sees opportunities in ammonia, the combustion of which does not release any climate-damaging CO2.
No suitable engines yet
Engines that can handle these alternative fuels are still in the development phase, however. Therefore, the infrastructure at the LEC has been expanded by about 1.2 million euros to advance research into ammonia combustion in large engines, such as those used in shipping. The ammonia infrastructure that has been set up is unique in Europe and among the first in the world, emphasised those responsible.