SHORT NEWS
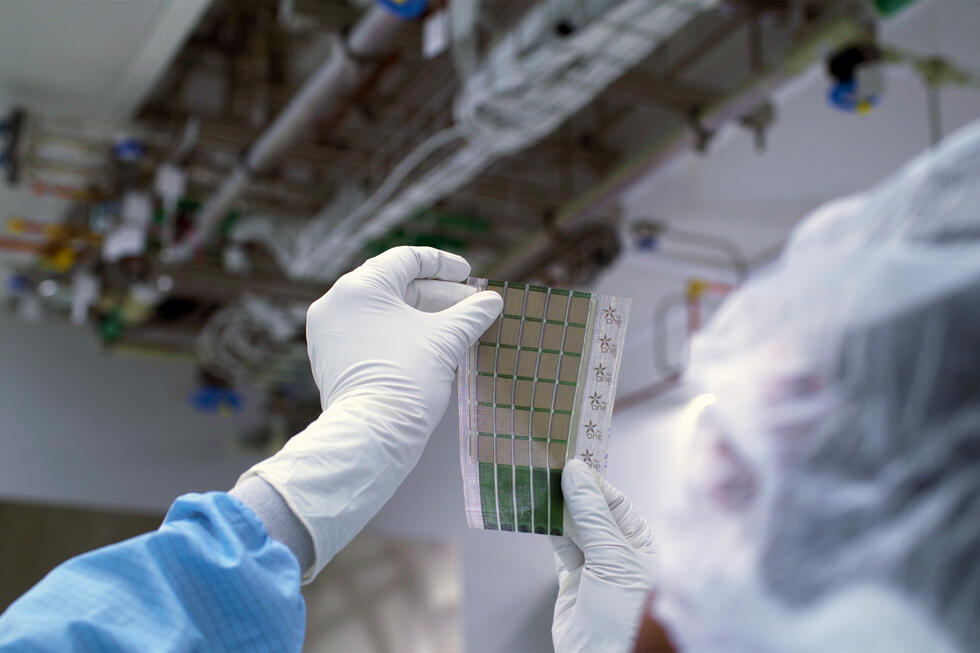
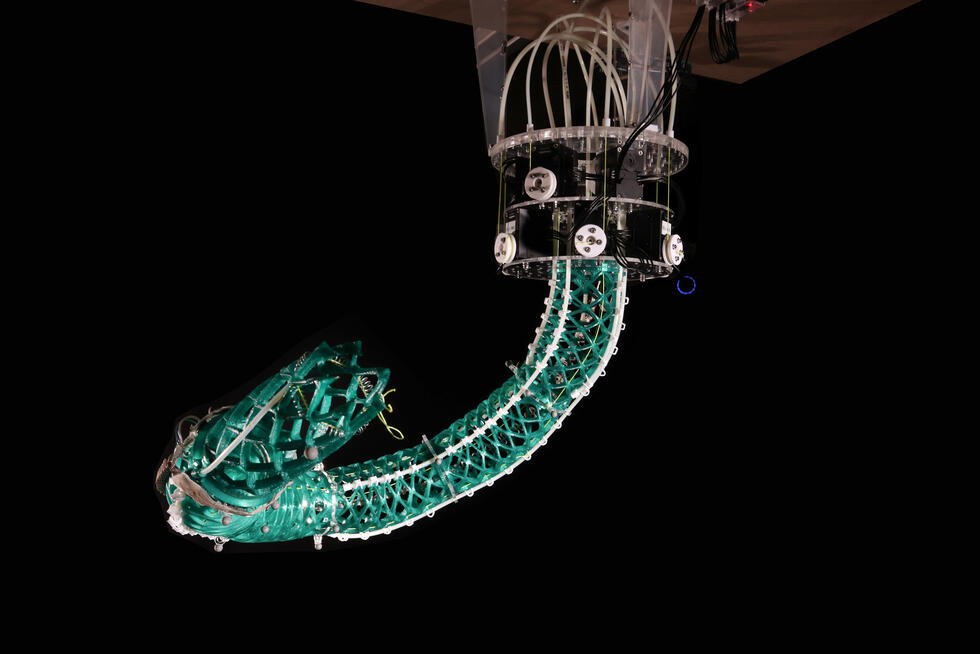
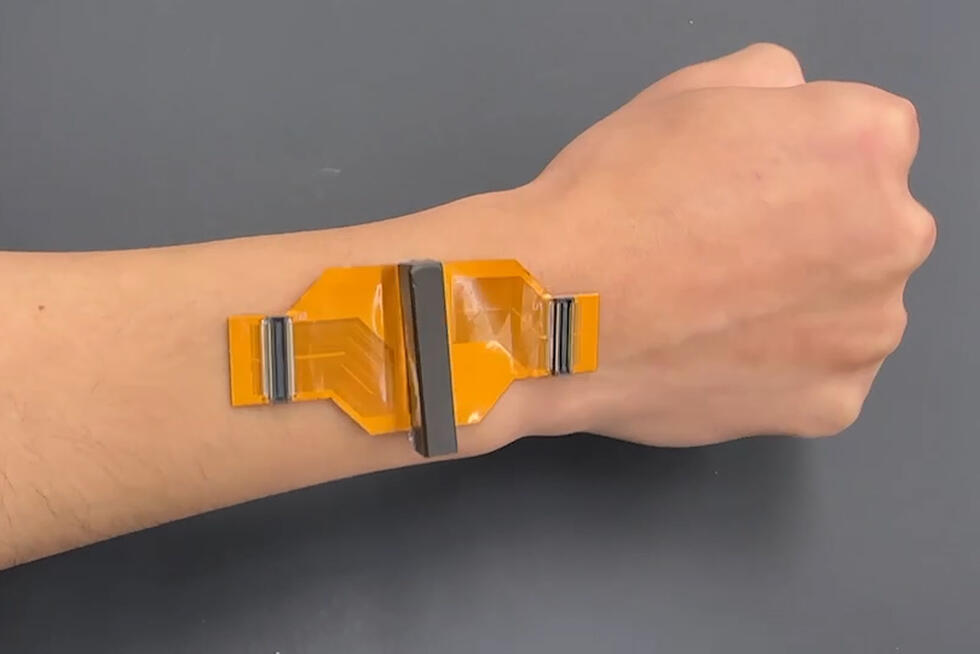
Like Lego: child's play to assemble stretchable devices
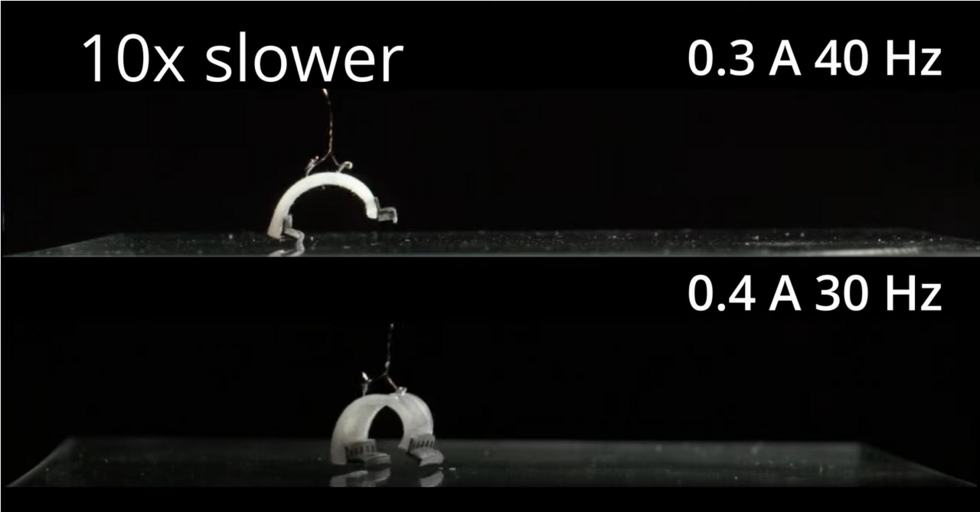
An international team led by researchers at NTU in Singapore has developed a universal connector that allows stretchable devices to be assembled easily and quickly using the Lego principle.
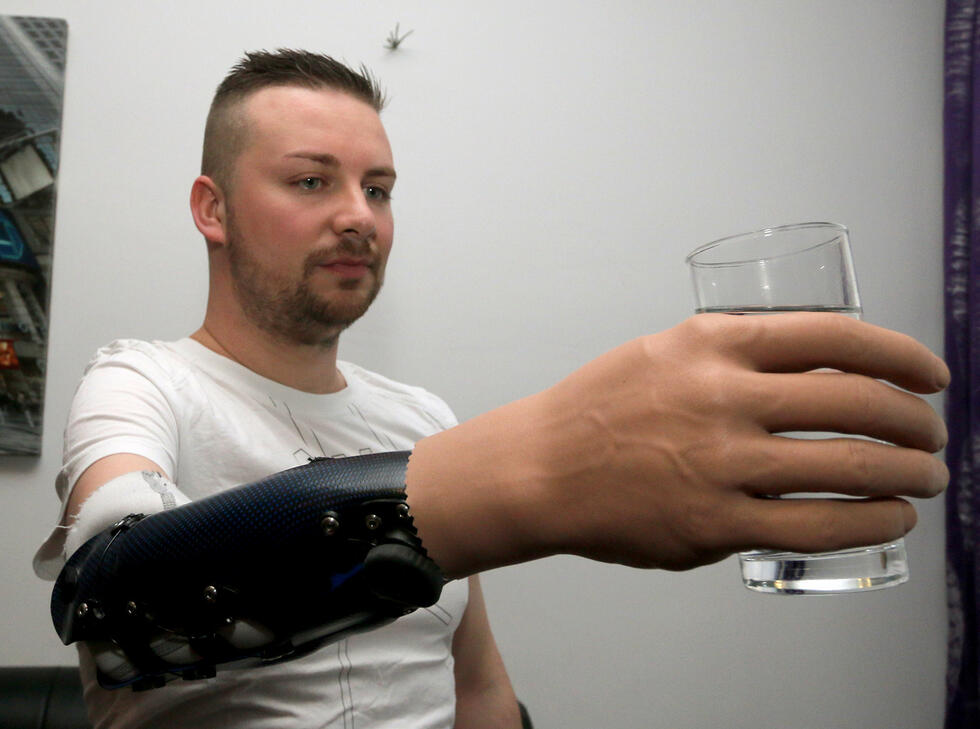
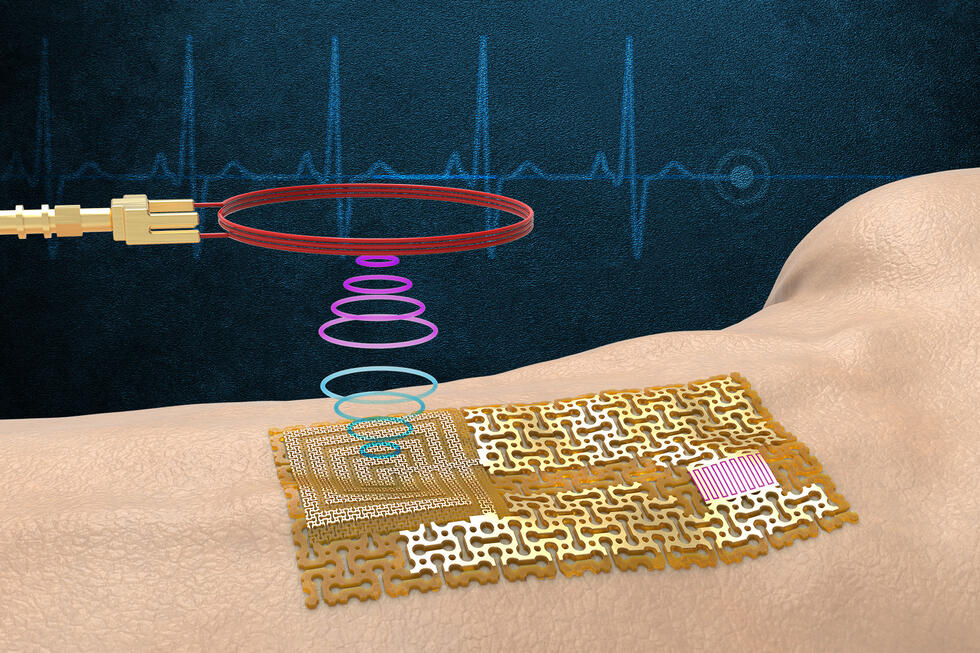
Stretchable devices such as soft robots and wearable health devices are assembled from several different modules with different material properties – some soft, some rigid and some encapsulated.
However, the commercially available adhesives currently used to connect the modules often do not reliably transmit mechanical and electrical signals when deformed, or break easily. Producing easily assembled, stretchable devices without compromising their strength and reliability under stress has long been a challenge that has limited their development.
Plugging modules together
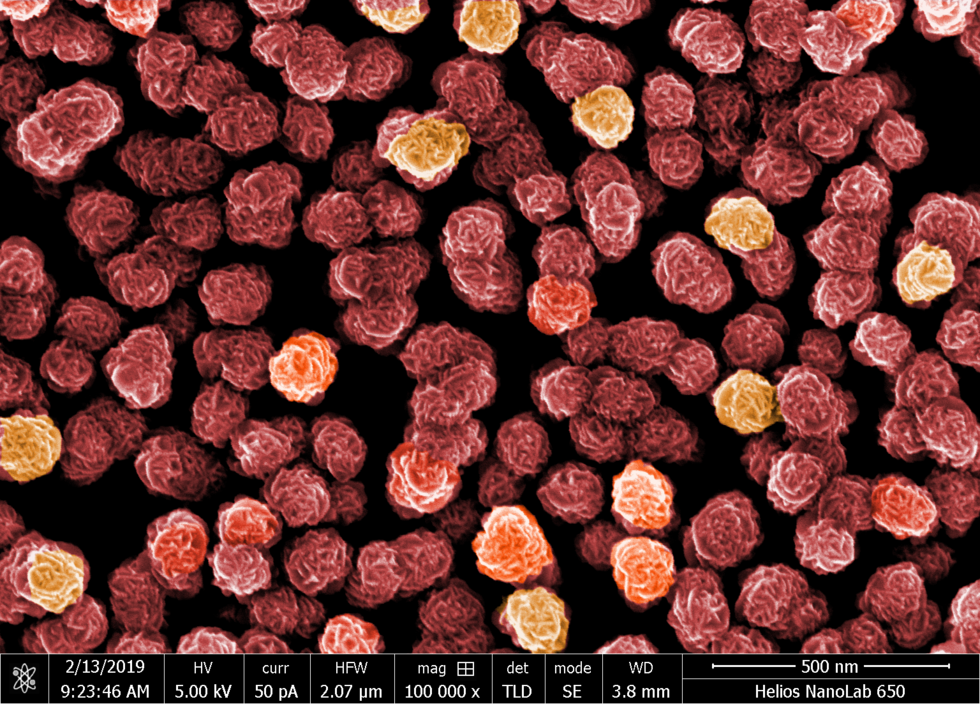
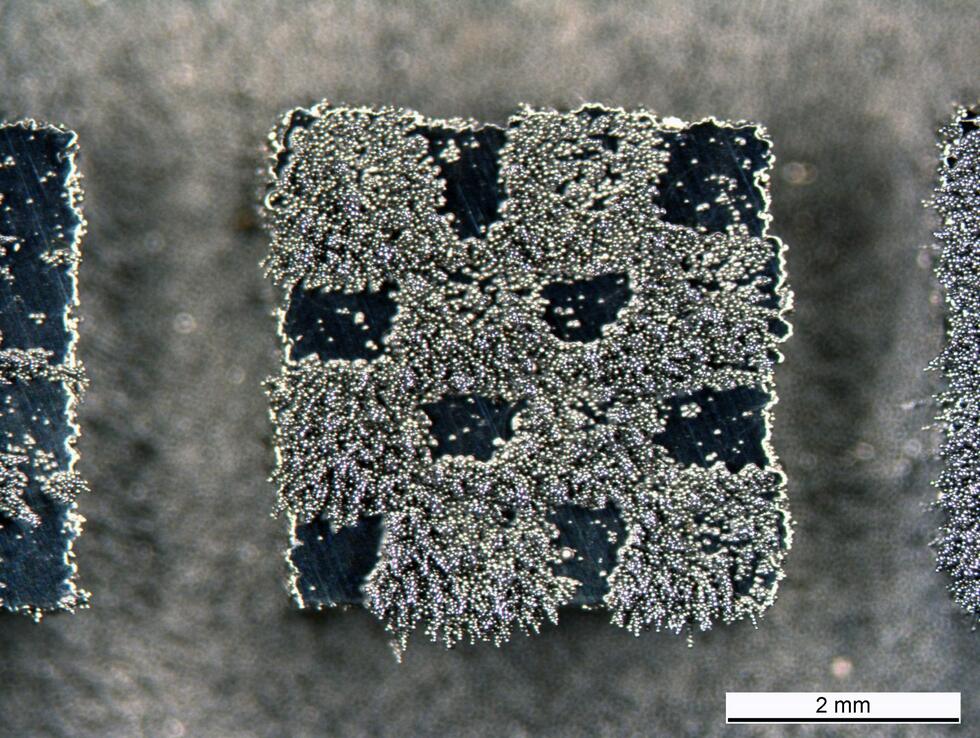
NTU says it has now developed an answer to this challenge and reported on it in the journal Nature: The BIND (biphasic nanodisperse interface) interface simplifies the assembly of stretchable devices while providing excellent mechanical and electrical performance.
Similar to building structures with Lego bricks, high-performance stretchable devices can be assembled by simply plugging modules together with the BIND interface. This convenient way of connecting electronic modules could form the basis for assembling future stretchable devices where manufacturers can "plug" components together as they see fit.